What’s the Difference Between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes?
Diabetes is one of India’s fastest-growing health concerns, with more than 100 million people currently living with the condition. Yet many patients still do not understand the difference between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, two conditions that may sound similar but work very differently inside the body.
Whether you are newly diagnosed, caring for a family member, or simply educating yourself, this guide explains key differences, symptoms, causes, treatment options, and prevention methods in the simplest way possible.
What Is Type 1 Diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease. The body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, leaving the body with little or no insulin.
- Usually diagnosed in children, teenagers, or young adults
- Not caused by diet or lifestyle
- Requires lifelong insulin therapy
- Cannot be prevented
- Symptoms often appear suddenly
People with Type 1 diabetes must take insulin daily through injections or an insulin pump. With proper care and monitoring, they can lead healthy, active lives.
What Is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes in India. It develops when the body becomes insulin-resistant or does not produce enough insulin.
- Usually develops in adults over 40, but now seen even in younger adults and children
- Strongly linked to unhealthy diet, physical inactivity, obesity, stress, and family history
- Managed with diet, exercise, oral medicines, and sometimes insulin
- Often preventable through lifestyle changes
- Develops slowly, sometimes without noticeable symptoms
Due to late diagnosis in many cases, it may go unnoticed for years unless regular screening is done.
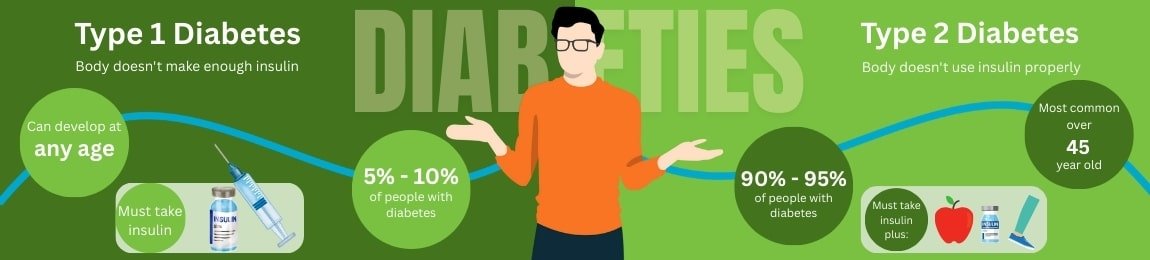
Type 1 vs Type 2 Diabetes: Key Differences
Here’s a quick comparison to help you understand how these two types differ:
| Feature | Type 1 Diabetes | Type 2 Diabetes |
| Usual Age of Onset | Childhood or adolescence | Adults over 40, but increasingly younger |
| Cause | Autoimmune destruction of insulin cells | Insulin resistance or poor insulin production |
| Insulin Production | Very little or none | Often reduced or not used effectively |
| Treatment | Always needs insulin | Diet, exercise, tablets, insulin (if needed) |
| Can it Be Prevented? | No | Often, through lifestyle changes |
| Speed of Onset | Sudden | Gradual |
| Prevalence in India | Less common (~5–10%) | Very common (~90% of diabetes cases) |
Symptoms of Diabetes to Watch For
The symptoms of diabetes can be subtle or severe. If you notice any of the following, it’s time to see a doctor:
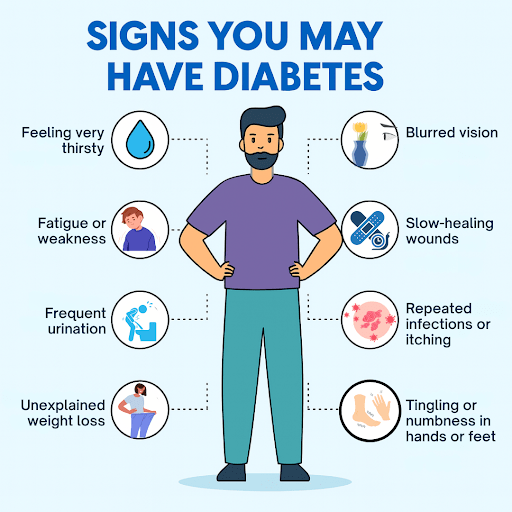
- Feeling very thirsty
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue or weakness
- Unexplained weight loss
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing wounds
- Repeated infections or itching
- Tingling or numbness in hands or feet
Early diagnosis can prevent complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, nerve issues, and vision problems.
Managing Diabetes
Both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes can be managed effectively with the right guidance.
For People Living with Diabetes:
- Eat a healthy, balanced diet with whole grains and vegetables
- Exercise regularly (walking, yoga, cycling, etc.)
- Monitor blood sugar levels consistently
- Take insulin or medicines as prescribed
- Go for routine check-ups, especially for eyes, kidneys, and heart
- Seek advice from diabetes specialists, dietitians, and counsellors
For People Looking to Prevent Diabetes:
- Maintain a healthy body weight
- Avoid sugary, oily, and processed foods
- Stay physically active for at least 30 minutes daily
- Get regular diabetes screening if you have a family history
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can Type 2 diabetes turn into Type 1?
No. They are completely different conditions and one cannot convert into the other.
2. What test is done to confirm diabetes?
3. Is Type 1 diabetes genetic?
4. Can Type 2 diabetes be reversed?
5. Which type of diabetes is more common in India?
Understanding the difference between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes can help you take the right steps, whether that’s getting tested, adjusting your lifestyle, or supporting a loved one.
If you are experiencing symptoms or want to understand your diabetes risk, you can consult our expert diabetologist at Synergy Multispeciality Hospital, Nagpur. Early diagnosis and the right management plan can prevent long-term complications and help you live a healthier life.



.svg)
.svg)



