Prostate Health Matters: Early Detection and Management of Prostate Problems
The prostate is an important gland in a man’s body, yet many men hesitate to talk about prostate health. As we grow older, the prostate naturally undergoes changes. Some are harmless, but others may lead to problems such as prostate enlargement, infections, or even prostate cancer. What makes prostate issues concerning is that many of them develop quietly without early symptoms.
In this blog, we explain the most common prostate problems, early warning signs, tests used for diagnosis, and simple lifestyle measures men can follow to keep their prostate healthy.
Understanding the Prostate and Its Functions
The prostate gland is located below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It surrounds the urethra—the tube through which urine passes.
Its main function is to produce seminal fluid, which helps nourish and transport sperm.
As men age, the prostate may increase in size or become prone to infections and other conditions. Recognising these changes early can help prevent complications and ensure better treatment outcomes.
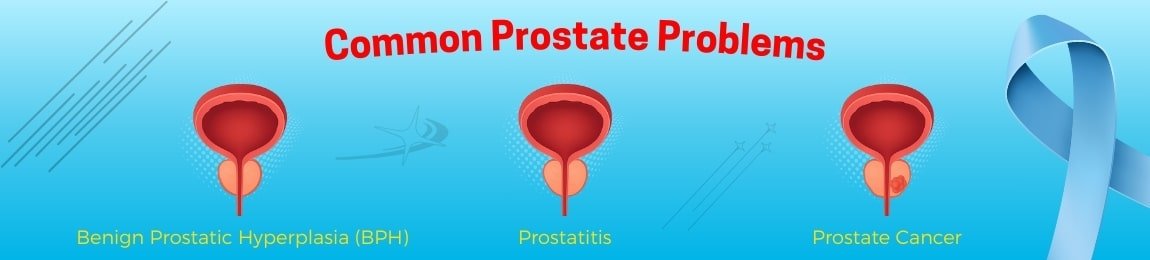
Common Prostate Problems
1. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
BPH, commonly known as prostate enlargement, is a non-cancerous condition seen mostly in men above the age of 50.
Common symptoms include:
- Frequent urination
- Difficulty starting urination
- Weak urine flow
- Feeling of incomplete bladder emptying
BPH is not life-threatening, but it can disturb day-to-day life if ignored.
2. Prostatitis
Prostatitis refers to inflammation or infection of the prostate. Men of all age groups can experience it.
Symptoms include:
- Pelvic or lower abdominal pain
- Painful urination
- Flu-like symptoms
- Pain or discomfort during ejaculation
Prostatitis may be acute or chronic and often requires targeted medical treatment.
3. Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is one of the most commonly diagnosed cancers among men.
Risk factors include:
- Increasing age (especially after 50)
- Family history
- Certain ethnic backgrounds
In the early stages, prostate cancer may not cause symptoms. As it progresses, men may experience:
- Blood in urine
- Frequent urination
- Difficulty passing urine
- Bone pain (in advanced cases)
Why Early Detection Is Important
Many prostate conditions, especially prostate cancer, show little to no symptoms in the beginning. Early screening helps detect problems before they become serious.
Common Screening Tests
PSA Test (Prostate-Specific Antigen):
A simple blood test that checks PSA levels. Higher levels may indicate prostate problems.
Digital Rectal Examination (DRE):
A physical examination where a doctor checks the size and texture of the prostate.
Imaging or Biopsy:
If abnormalities are found, ultrasound, MRI, or a biopsy may be recommended to confirm the diagnosis.
Early detection greatly improves treatment success and helps prevent complications.
Treatment and Management Options
BPH (Prostate Enlargement):
- Lifestyle changes: Reduce caffeine, limit fluids at night
- Medicines: Alpha-blockers or 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors
- Surgery: Procedures like TURP may be recommended for severe symptoms
Prostatitis:
- Antibiotics: For bacterial infections
- Pain management: Warm baths, hydration, and light exercises
- Chronic cases: May need long-term evaluation and treatment
Prostate Cancer:
Treatment depends on the stage and severity.
- Active surveillance: For small, slow-growing cancers
- Surgery: Such as prostatectomy
- Radiation therapy or hormone therapy
- Advanced treatments: Targeted therapies and immunotherapy
Lifestyle Tips for Better Prostate Health
Simple everyday habits can go a long way in supporting prostate health.
- Healthy diet: Tomatoes, broccoli, nuts, whole grains, and fish rich in omega-3
- Regular exercise: Helps maintain healthy weight and lowers risk
- Limit smoking and alcohol: Both can worsen prostate-related issues
- Routine health check-ups: Especially for men above 50 or those with family history
Mental Health and Prostate Issues
Dealing with prostate problems can cause anxiety, embarrassment, or even depression. Men often hesitate to seek help due to stigma or fear. Encouraging open conversations and seeking professional guidance can improve both mental and physical well-being. Support groups, counselling, and open discussions with healthcare professionals play a crucial role in holistic management.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. At what age should men start prostate screening?
Men should begin prostate screening at 50 years.
If there is a family history of prostate cancer, screening may be recommended from 45 years or earlier.
2. Is prostate enlargement the same as prostate cancer?
3. What is the PSA test and why is it important?
4. Can prostate problems be treated without surgery?
5. Does every man with prostate cancer need surgery?
6. When should I consult a urologist?
Conditions like BPH, prostatitis, and prostate cancer are common but manageable when detected early. Staying informed, recognising symptoms, and going for regular screenings can protect your health in the long run.
If you are experiencing symptoms—or if you are above 50—it is wise to meet a qualified specialist. For proper diagnosis and advanced treatment, consulting the best urologist in Nagpur can help you receive timely care and prevent complications.
Taking small proactive steps today can lead to a healthier and stronger tomorrow. Don’t wait for symptoms to appear—early detection is the best protection.



.svg)
.svg)



